When losing weight, you will hear about medium-chain triglycerides and ketogenic diets. Medium-chain triglycerides are a new type of functional food ingredient: glycerol composed of saturated medium-chain fatty acids with a carbon chain length of 6-12 triglycerides, which are mainly derived from palm kernel oil, coconut oil, milk, and their products, having unique metabolic pathways.
1. Medium chain triglycerides and Ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet is high in fat, low in carbohydrates, and formulated with appropriate protein and other nutrients.
The main principle of the ketogenic diet: replace carbohydrates (rice, flour, and sugar) with fat. After the body consumes the glucose, it slowly starts to burn fat to supply energy to the body. The body slowly enters a ketogenic state, and finally, let the body enters a state of high-speed fat burning.
slowly starts to burn fat to supply energy to the body. The body slowly enters a ketogenic state, and finally, let the body enters a state of high-speed fat burning.
The medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) diet is a modified ketogenic diet that replaces long-chain fatty acids with medium-chain fatty acids (which produce higher amounts of ketone due to faster absorption and utilization of medium-chain fatty acids). Reducing the total amount of fat allows for a higher ratio of carbohydrates to protein.
2. Medium Chain Triglycerides and Weight Loss
Because the gastrointestinal tract absorbs medium-chain triglycerides (MCT), they can be metabolized very quickly by the liver, rapidly activating the body’s fat-burning factors, also known as ketone bodies, to accelerate the body’s burning of fat, so as to achieve the goal of weight loss. When studying the effect of MCT on weight loss and body composition, a randomized controlled trial was conducted in healthy adults for three consecutive weeks, and it was found that compared with the LCT group, the MCT group lost weight (p<0.001) and reduced waist circumference (p<0.001), hip circumference (p=0.002), total body fat (p<0.001), visceral fat (p<0.001), total fat (p<0.001). MCTs  reduce appetite and increase satiety, resulting in more significant weight loss and fat oxidation.
reduce appetite and increase satiety, resulting in more significant weight loss and fat oxidation.
3. Metabolic characteristics of medium-chain triglycerides
Fast Digestion Rate (i.e., hydrolysis rate)
Triglyceride is mainly in the small intestine; through the action of bile acid, it is emulsified into fine colloidal droplets, under the activity of pancreatic lipase, hydrolyzed into two molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of monoglycerides, which are then absorbed by intestinal epithelial cells.
Due to the relatively strong hydrophilicity of medium-chain triglycerides, the formed emulsified colloidal droplets are smaller. They require less emulsifier (i.e., bile acid), so hydrolysis is more likely to occur. In other words, medium-chain triglycerides are digested faster than long-chain triglycerides.
Fast Absorption
Medium-chain fatty acids take only a few minutes to be absorbed directly from the intestinal epithelium and enter the blood circulation through the hepatic portal vein.
The long-chain fatty acids need to be re-combined with glycerol to form triglycerides in intestinal epithelial cells; and form chylomicrons with apolipoproteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol, and enter the blood circulation through the lymphatic system. It takes 3 to 4 hours to complete the process. Therefore, medium-chain triglycerides are absorbed faster than long-chain triglycerides and are a nutrient that can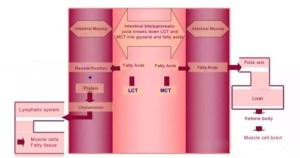 provide energy quickly.
provide energy quickly.
Quick Energy Generation
In liver and muscle tissue, fatty acid catabolism occurs within the mitochondria of cells. Unlike long-chain fatty acids, medium-chain fatty acids enter the mitochondria without being carried by the L-carnitine shuttle system. Alternatively, their catabolism is not restricted by the L-carnitine shuttle system.
As a result, medium-chain fatty acids are more prone to oxidation than long-chain fatty acids and can provide thermal energy at any time without being easily stored. In addition, due to the relatively short chains of medium-chain fatty acids, they cannot be used as structural materials for adipocytes without the occurrence of metabolic reactions to lengthen the carbon chain.
As a high-quality fat powder, medium-chain triglyceride oil powder has been widely used in various food and functional products.


Leave A Comment